
Models are constructed in such a way that users can modify existing components or write their own, extending the capabilities of the environment.Īfter 35 years of commercial availability, TRNSYS continues to be a flexible, component-based software package that accommodates the ever-changing needs of both researchers and practitioners in the energy simulation community. The standard library includes approximately 150 models ranging from pumps to multizone buildings, wind turbines to electrolyzers, weather data processors to economics routines, and basic HVAC equipment to cutting edge emerging technologies. The second part of TRNSYS is an extensive library of components, each of which models the performance of one part of the system.
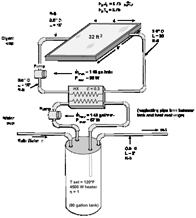
The kernel also provides utilities that (among other things) determine thermophysical properties, invert matrices, perform linear regressions, and interpolate external data files. This thesis is an analysis of the simulated performance of two indirect heat pump assisted solar domestic hot water (i-HPASDHW) systems compared to two base systems: an electric domestic hot water (DHW) system and a traditional solar domestic hot water (SDHW) system. NOMENCLATURE c p specific heat capacity, J/gK C heat capacity, J/K d diameter, m f save fractional energy savings g gravity constant, m/s2 h storage height, m M& mass flow rate, kg/s P power (of burner and el. The first is an engine (called the kernel) that reads and processes the input file, iteratively solves the system, determines convergence, and plots system variables. While the vast majority of simulations are focused on assessing the performance of thermal and electrical energy systems, TRNSYS can equally well be used to model other dynamic systems such as traffic flow, or biological processes. On the other hand, the comparison of levelized cost of energy shows that Tangier is the city with the greatest potential for wind energy system and other cities are expected to present a challenge since the areas for efficient on-site generation of photovoltaic and solar thermal collectors are limited.TRNSYS (pronounced 'tran-sis') is an extremely flexible graphically based software environment used to simulate the behavior of transient systems. Moreover, 45% of building energy load can be covered instantly by renewable energy systems in all Moroccan climatic zones.

More than 21% of energy saving can be achieved, 28% in heating load and 40% in cooling. b) Water heaters Types: Type 6: Auxiliary heater (used as Electric ITWH) Type 6 models an auxiliary heater that elevates the temperature of a flow stream to a set point temperature, by setting a maximum heating rate. The obtained results show that the application of the multi-objective study conclusions combined with an efficient use of renewable energies makes it possible to achieve zero energy building throughout all Moroccan housing stock. This was a very useful tool for unit conversion from TRNsys outputs units to the International System of Units. A multi-objective optimization has been carried out in order to find the best solution which will allow a compromise between the building life cycle cost, energy saving and thermal comfort through the optimization of the aforementioned design parameters as passive energy efficiency measures.
#Trnsys sdhw auxillary heating windows
The design features considered include building orientation, windows type and Window-to-Wall Ratio, wall and roof insulation and infiltration rate. The impacts of retrofitting an existing residential building to meet zero energy balance in the six Moroccan climatic zones have been investigated. The present study aims to assess the possibility of achieving net zero energy building in the Moroccan housing stock by combining architectural energy efficiency practices and renewable energies for hot water and electricity productions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
